Enzyme Properties And Functions
Enzyme Properties And Functions. Lyases catalyze the breakdown of various chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis and oxidation, often forming new double bonds or ring structures. The activity of enzymes depends upon the acidity of medium (ph specific).

 PPT Properties of Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free from www.slideserve.com
PPT Properties of Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free from www.slideserve.comEnzymes are proteins that are found in all living organisms. Ribozyme is an rna molecule. Isomerases catalyze structural shifts in molecules, causing changes in shape.
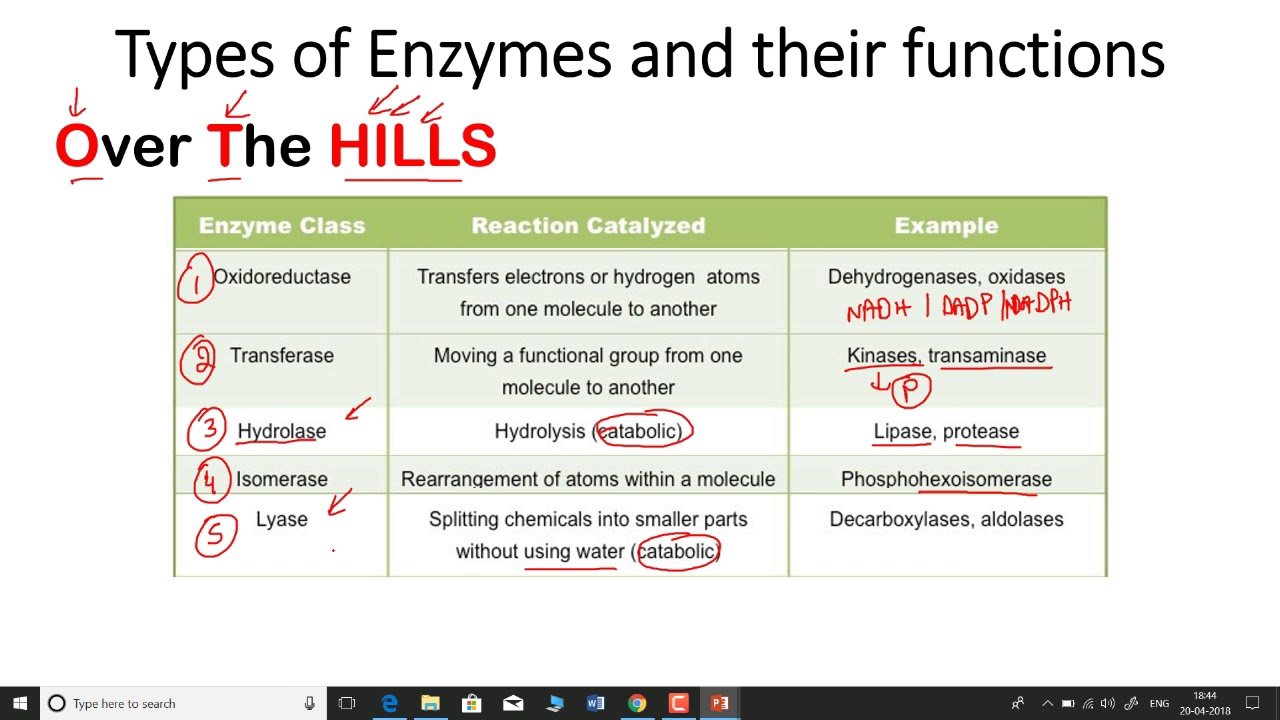
All enzymes are protein in nature except ribozyme. Enzymes are produced by cells but the presence of cell is not essential for their activity.
Ribozyme is an rna molecule. Ph 2 for pepsin, ph 8.5 for trypsin, for example.
All enzymes are protein in nature except ribozyme. Enzymes are often referred to as the biological catalysts.

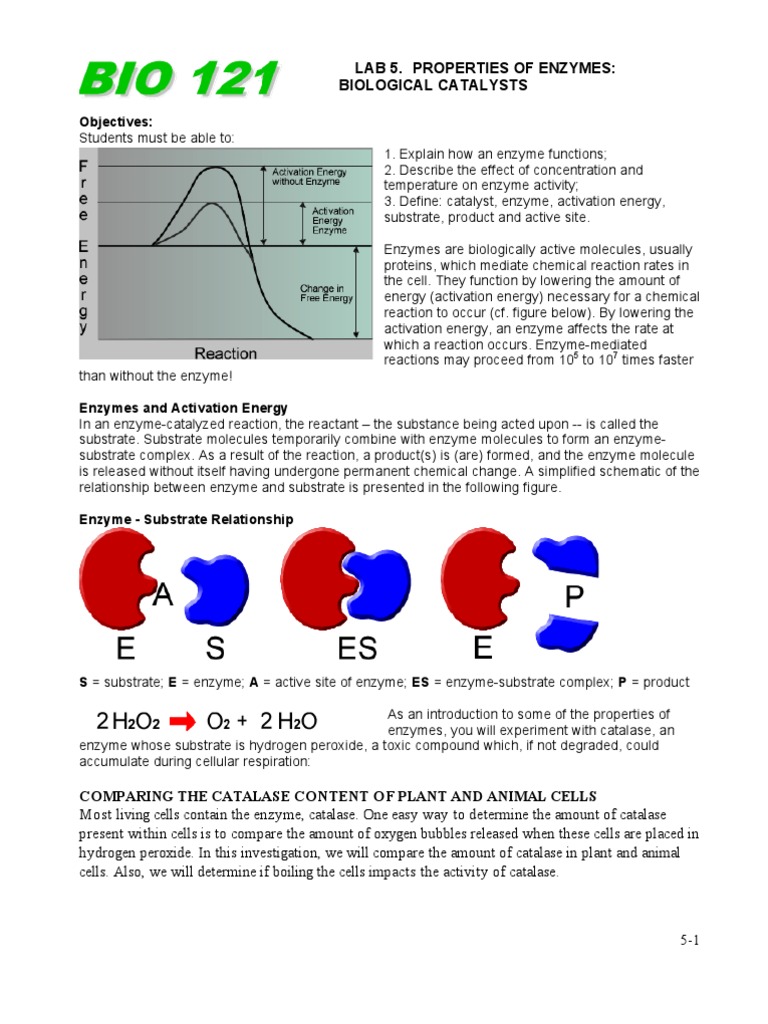
Therefore, it is clear that enzyme lowers the free energy of activation (∆g ≠) for a biochemical reaction by more than 50% due to following reasons: The enzyme is a substance that performs as a biological organic catalyst to enhance the chemical reactions.
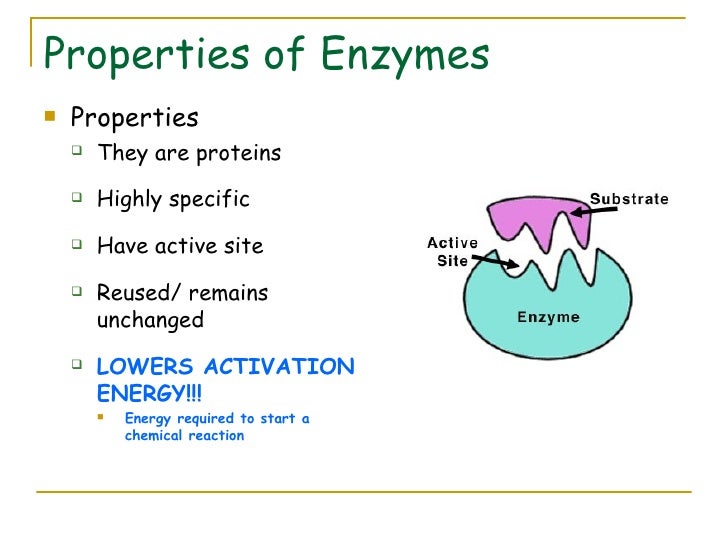
Their presence does not effect the nature and properties of end product. On biological aspects, enzymes are instrumental substances to many functions in living organisms.

They affect every function, from breathing to digestion. The activity of enzymes depends upon the acidity of medium (ph specific).
All enzymes are protein in nature. Catalase has two enzymatic activities depending on the concentration of h2o2.

On biological aspects, enzymes are instrumental substances to many functions in living organisms. The activity of enzymes depends upon the acidity of medium (ph specific).
/what-is-enzyme-structure-and-function-375555_v4-6f22f82931824e76b1c31401230deac8.png)
(i) raising the ∆g of the substrate, (ii) stabilizes the transition state, Most intracellular enzymes function at near neutral ph.

Ribozyme is an rna molecule. This includes increasing the efficiency of chemical reactions, making energy molecules called atp, moving components of the cell and other substances, breaking down molecules (catabolism) and building new molecules (anabolism).

Ø a small amount of enzyme is enough to convert a large quantity of substrates. Enzymes initiate and accelerate the rate of biochemical reaction.
![PPT Human Biochemistry [Option B] B7 Enzymes Objectives](https://image3.slideserve.com/5729155/basic-characteristics-of-enzymes-cont-d-n.jpg)
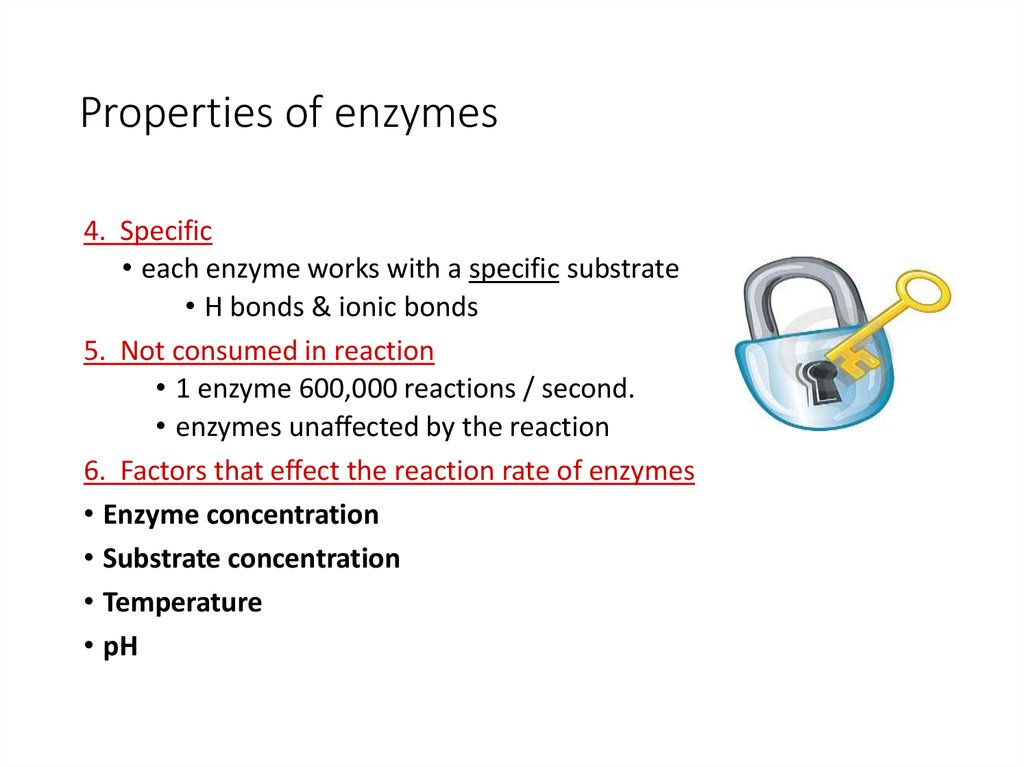
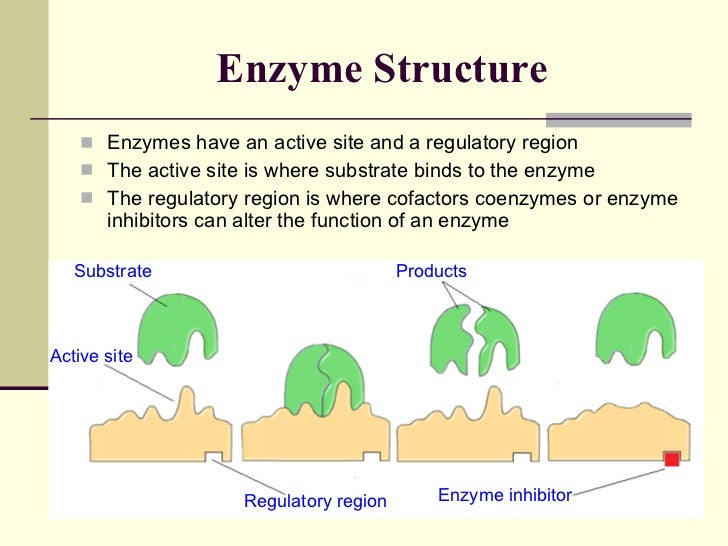
Enzymes perform a number of biochemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, etc. This cleft or pocket is known as active site of enzyme.
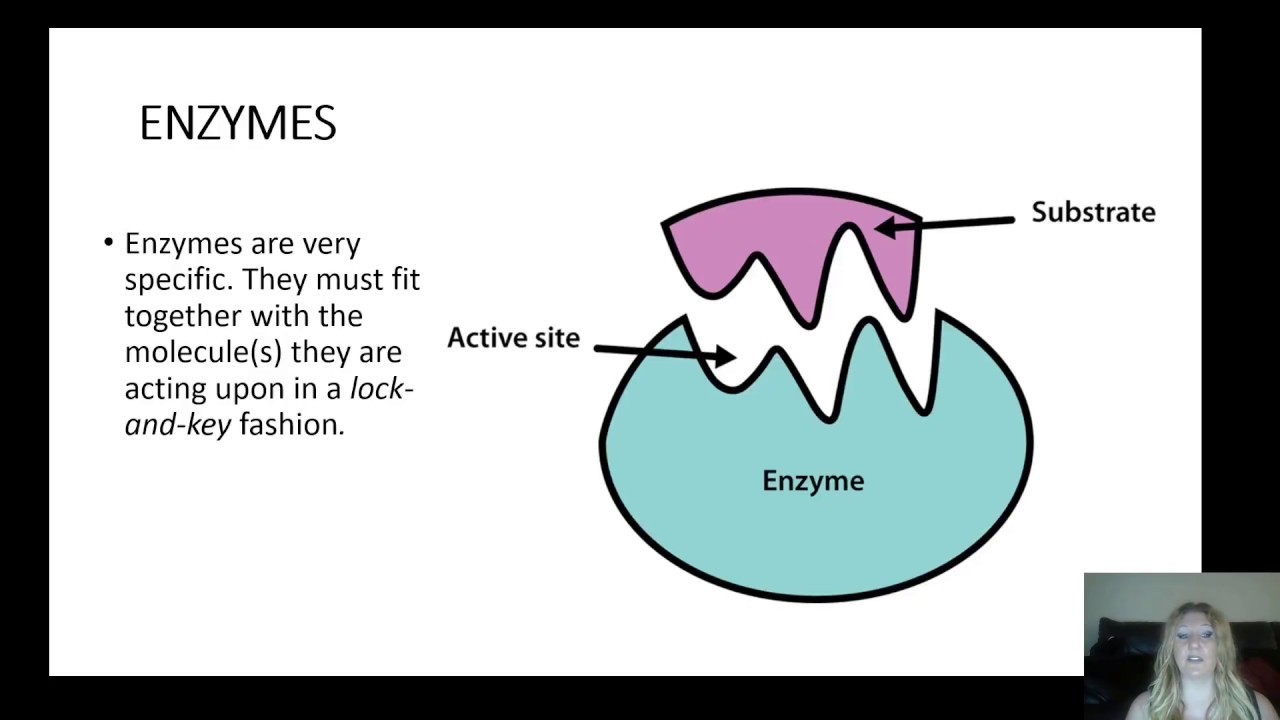
Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the body. Its function is to speed up metabolic reactions.
Enzymes initiate the biochemical reaction rate and accelerate it. (i) raising the ∆g of the substrate, (ii) stabilizes the transition state,
The activity of enzymes depends on the medium acidity of the (ph specific). Removes h2o2 by forming h2o and o2.
Enzymes perform a number of biochemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, etc. Removes h2o2 by forming h2o and o2.
The enzyme is a substance that performs as a biological organic catalyst to enhance the chemical reactions. This cleft or pocket is known as active site of enzyme.
1) to accelerate or retard or bring about reaction 2) regulate reaction 3) to make possible the metabolic reactions 4) to facilitate reaction 5) to break down larger molecule to small molecule 6) to carry out flow of reaction smoothly All enzymes are protein in nature except ribozyme.
Their presence does not effect the nature and properties of end product. The general name that chemists use for a chemical entity that increases the speed of a reaction is a "catalyst.".
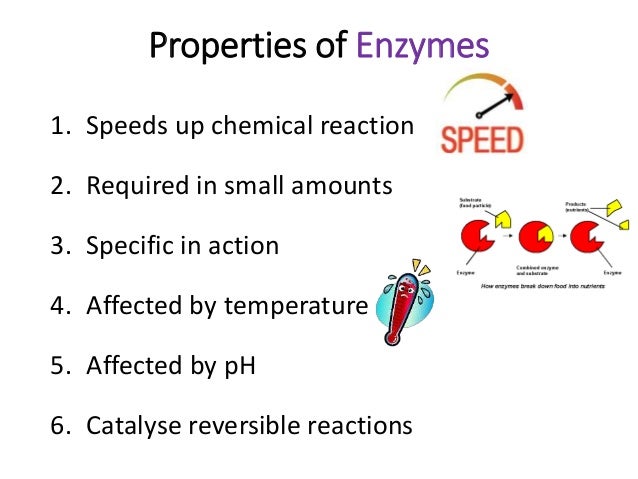
Ø a small amount of enzyme is enough to convert a large quantity of substrates. They are highly specific in their action that is each enzyme can catalyze one kind of substrate.
For Example, The Food That You Eat Is Broken Down By Digestive Enzymes Into Tiny Pieces That Are Small Enough To Travel Through Your Blood Stream And Enter Cells.For example, ph 2 for pepsin, ph 8.5 for trypsin. The enzymes are organic catalysts or biocatalysts which catalyse biochemical reactions at a specific biological temperature. They create the conditions needed for biochemical reactions to happen fast.
Enzyme Activity Can Be Regulated, Varying In Response To The Concentration Of Substrates Or Other Molecules.Most intracellular enzymes function at near neutral ph. The presence of the enzyme in the resin ducts of anacardiaceae indicates a defense function against herbivores, predators, and bacterial and fungal invasion. Removes h2o2 by forming h2o and o2.
This Includes Increasing The Efficiency Of Chemical Reactions, Making Energy Molecules Called Atp, Moving Components Of The Cell And Other Substances, Breaking Down Molecules (Catabolism) And Building New Molecules (Anabolism).Their presence does not effect the nature and properties of end product. Enzymes catalyze all kinds of chemical reactions that are involved in growth, blood coagulation, healing, diseases, breathing, digestion, reproduction, and many other biological activities. Ø the enzymes remain unchanged after the reaction.
Therefore, It Is Clear That Enzyme Lowers The Free Energy Of Activation (∆G ≠) For A Biochemical Reaction By More Than 50% Due To Following Reasons:Ph 2 for pepsin, ph 8.5 for trypsin, for example. Structure and function enzymes act as the body'scatalysts bycomplexing thereaction'sparticipants in the correct arrangement to react, lowering the activation energy, e a, to react, but g stays the same. [properties and functions of enzymes].
Joanna Holds A Phd In Biology From The University Of Michigan And Is Currently Working Towards A.This article presents short review about structure, properties and functions of the above enzymes in living cells. [article in german] schmidt b. 1) to accelerate or retard or bring about reaction 2) regulate reaction 3) to make possible the metabolic reactions 4) to facilitate reaction 5) to break down larger molecule to small molecule 6) to carry out flow of reaction smoothly
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Enzyme Properties And Functions"
Posting Komentar